What is shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis is inflammation of the bursa in your shoulder. The bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between a bone and a tendon. A tendon is a cord of strong tissue that connects muscles to bones.
Bursitis is more common in adults, especially in those over 40 years of age.
These Parts of the Body can affected by Bursitis: Elbow, Shoulder, Hip, Knee and Achilles tendon.
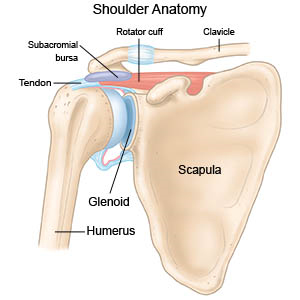
What causes shoulder bursitis?
- An injury, such as a fall
- Bacterial infection
- Overuse of the shoulder, such as when you paint or swim
- Bony growths that rub against and irritate the bursa and tendons
What are the signs and symptoms of shoulder bursitis?
- Pain when you move your shoulder or raise your arm over your head
- Decreased movement of your arm and shoulder
- Redness or swelling
- Crunching or popping when you move your shoulder
- Shoulder and arm weakness
How is shoulder bursitis diagnosed?
Your caregiver will examine your shoulder and ask about your injury or activities. You may need any of the following:
- Blood tests
- X-rays
- MRI
- Fluid culture
How is shoulder bursitis treated?
- NSAID drugs: These medicines decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs are available without a doctor’s order. Ask your caregiver which medicine is right for you. Ask how much to take and when to take it. Take as directed. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding and kidney problems if not taken correctly
- Antibiotics: These help fight an infection caused by bacteria. You may need antibiotics if your bursitis is caused by infection.
- Steroid injection: This shot will help decrease pain and swelling.
- Bursectomy: This is surgery to remove your bursa. It is only done when other treatments do not work.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Rest: Rest your shoulder as much as possible to decrease pain and swelling. Slowly start to do more each day. Return to your daily activities as directed.
- Ice: Ice helps decrease swelling and pain. Ice may also help prevent tissue damage. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel and place it on your shoulder for 15 to 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times each day, as directed.
- Heat: Heat helps decrease pain and stiffness. Apply heat on the area for 15 to 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times each day, as directed.
- Sleep position: Try to avoid lying on your injured shoulder. You may be more comfortable if you sleep on your stomach or back.
- Physical therapy: You may need to see a physical therapist to teach you special exercises. These exercises help improve movement and decrease pain. Physical therapy can also help improve strength and decrease your risk for loss of function.
Resource:
http://www.drugs.com/cg/shoulder-bursitis.html
http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/arthritis-bursitis