زانو درد اختلال شایعی است که در هرکدام از ساختارهای استخوانی زانو اعم از مفصل زانو (استخوان ران، درشت نی، نازک نی) ، کاسه زانو (کشکک زانو) یا این که رباط ها و غضروف هاوومینیسک زانو بهوجود می آید. اکثر زمان ها مشکلات زانو به خوبی به روشهای درمانی محافظه کارانه عکس العمل نشان میدهند و به جراحی نیاز ندارند.
علل درد زانو:
شایعترین علل درد زانو که نیاز به اینترونشن دارند مشتمل بر:
1-آرتروز زانو: درانتهای استخوان مفاصل یک لایه غضروف است که موجب تسهیل حرکت و ضربه گیری میشود. آرتروز موجب تخریب غضروف ها و تغییر بافت استخوانی زیرین و تشکیل زوائد استخوانی میگردد که بعضی اوقات قطع و شناور می گردند و در نهایت موجب کاهش فضای مفصلی،تغییرزاویه، درد و تورم میشود.
2- پارگی منیسک: منیسک یک غضروف C شکل با خواص ارتجاعی است که از زانو در سطح داخلی و خارجی مراقبت می نماید و ضربه گیر است و موجب پایداری مفصل می شود. پارگی منیسک زانو معمولاً پیآمد پیچ خوردن یا این که چرخیدن سریع زانوی خم شدهاست در ورزشکاران و هم با افزایش سن به چشم میخورد.
3-آسیب تاندون کشکک: پایین کشکک بوده و عضله چهار سر زانو به آن پیوند می خورد این تاندون بسیار سفت تقریباً ۲ سانتی متر پهنا دارد و وظیفه آن تقویت پا در کنار عضلههای چهار سر ران است.بزرگترین علائم آسیب بهاین تاندون احساس درد جلوی زانو است . فعالیتهای مکرر ورزشی نظیر ضربه زدن با پا و پرش , سبب ساز وارد شدن فشار زیادی بهاین تاندون پا می شود و منجر به التهاب،پارگیهای بسیار کوچک و درد زیر زانو می شود .
مطلب مرتبط:
درد کنار زانو چه علتی دارد و چگونه درمان میشود؟
علامتها:
علائم مشکلات زانو اکثر اوقات به آهستگی بهوجود می آیند و با گذشت زمان ارتقاء مییابد . علامتها و نشانهها شامل:
درد:مفصل در حرکت یا با فشار در گیر درد میگردد که براساس محل آسیب مکان درد گوناگون است.
خشکی مفصل: خشکی مفصل که هنگام بیداری صبحگاهی شدید است.
التهاب:مفصل چه بسا با وارد کردن فشار کم، دچار التهاب میگردد.
کاهش انعطاف:دامنه حرکتی مفصل محدود می شود.
قفل و خالی کردن زانو: گیر کردن مفصل در میانه حرکت زانو
کریپیتاسیون:احساس صدای سایش هنگام تکان
تشخیص علت درد زانو:
تشخیص زود هنگام مشکلات زانو سبب ساز جلوگیری از پیشرفت آسیب دیدگی میگردد. تشخیص شامل شرح حال , معاینه فیزیکی , آزمایشات و تصویربرداری های مورد لزوم است که مشتمل بر گرافیساده و جهت بررسی بافت نرم و ام آر آی است.
داروهای موءثر زانو درد:
از داروها جهت برطرف کردن نشانه ها در فاز حاد استفاده میشود که مشتمل بر تسکین دهنده های ضدالتهابی و ترکیبات غضروف ساز هست.
معالجه های غیر تهاجمی درد زانو:
فیزیوتراپی : در فیزیوتراپی ترکیبی از روشهای غیرفعال و تمرینها جهت تقویت ساختارعضلانی و حرکتهای اصلاحی به کار گرفته میشود. مدالیتههای درمانی غیرفعال مثل یخ/ گرما , اولتراسوند و تحریک الکتریکی درد و گرفتگی عضلانی را در کاهش می دهد. مریض مبتلا به کمک انجام تمرینهای منحصر به فرد روش افزایش انعطاف پذیری و دامنه حرکتی را فرا میگیرد و بر قدرت عضلات خویش که حمایت کننده زانومیباشند می افزاید. بیماران نباید از روی آوردن بهاین معالجه نگران باشند، چه بسا بیماران دچار درد و مشکلات حرکتی هم از انجام تمرین های ایزومتریک سود میبرند.
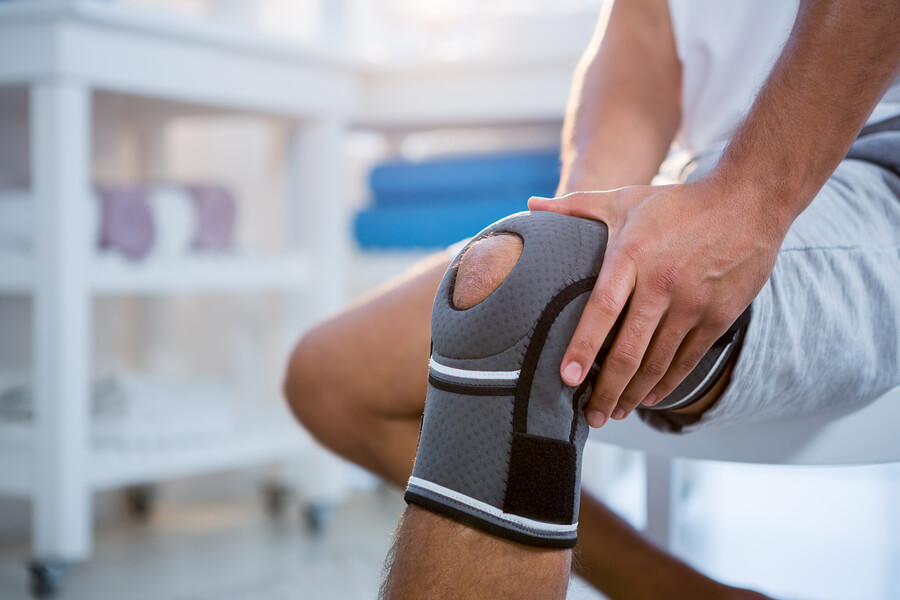
زانوبند طبی: استفاده از زانوبند یا بریس در فرآیند اولیه سبب ساز کاهش فشار روی زانو می شود و این امر درد و نشانه ها را تا حد متعددی کاهش میدهد .
کفی و کفش طبی: کفی های اختصاصی برای ایجاد هم ترازی زانو و کارایی بهتر کشکک زانو موثر میباشد و ممکن است از سمت دکتر برای مریض تجویز شود. پوشیدن کفش مناسب در معالجه این بیماری اهمیت زیادی دارد.
ماساژ و معالجه دستی و منیپولیشن: مبنا این تکنیک ها که به وسیله دست انجام می شود نیز تقویت ساختار عضلانی بافت های اطراف زانو میگردد.
لیزر پرتوان : به کار گیری از لیزر پرتوان پالس موجب ارتقا انرژی سلولی و ترمیم بافت های آسیب دیده و تا حدی جلوگیری از پیشرفت میشود.
معالجه های اینترونشنال و یا کمتر تهاجمی (مداخله ای)
اعمال اینترونشنال بوسیله فوق تخصص درد زیر راهنمایی اشعه ایکس ( فلوئوروسکوپی) و یا این که سونوگرافی در اتاق عمل انجام میشود که دربرگیرنده:
1- تزریق اوزون:روش معالجه زانو درد ناشی از آرتروز زانو با به کار گیری از تزریق اوزون برای انواع مشکلات زانو مفید و اثر گذار هست. در موارد ابتلا به آسیب دیدگی های زانو اعم از آرتروز زانو این روشدرمانی سبب ساز بهبود جریان خون در بافت آسیب دیده می شود و به این ترتیب با آماده کرد مواد مفید در بافت، سبب تسریع در بهبودی می شود. دراین روش ازون 25 میکروگرم به بافت آسیب دیده زانو تزریق می شود، و سبب از بین رفتن درد و تورم می شود و رسوبات فیبری را تحریک می نماید، تا باعث شود سلول ها با استفاده از این رسوبات، بافت آسیب دیده را ترمیم نمایند. تزریق اوزون می بایست هر ۱ الی ۲ هفته یکبار تکرار شود , بیماران بعداز یک الی دو جلسه درمانی به بهبودی و نتایج دلخواه (التیام درد و از بین رفتن تورم ) می رسند .
2-تزریق PRP : تزریق PRP یا پلاسمای غنی از پلاکت , یکی از از روش های درمانی مفید در معالجه آرتروز زانو هست. دراین روش پلاکت های غلیظ شده که دربردارنده فاکتورهای رشد سلولی می باشندتهیه و تزریق شده که در محیط تزریق شده مفصلی موجب جلوگیری از پروسه تخریب بافتی و ترمیم میشود. این روش عوارض جانبی ندارد چون پلاسمای غنی از پلاکت از خون خود مریض گرفته می شود.
3-تزریق ارتوکین: در روش ارتوکین , خون خود مریض گرفته شده و سرم آن پالایش می شود که دربردارنده آنتاگونیست اینترلوکین 1 است و موجب کاهش درد و التهاب بافت آسیب دیده و ترمیم آن می شود.
4-رادیوفرکوئنسی: از رادیوفرکوئنسی با مد پالس در جهت ترمیم مشکلات درون مفصل و هم تعدیل پیام عصبی انتقال درد(نرومدولیشن)اعصاب زانویی و… استفاده میگردد